Anatomy and Physiology
Subjects
Anatomy
Form of the body
Physiology
Function of the body
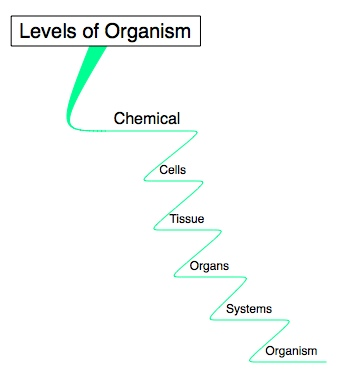
Main Proceses of Body
Catabolism
the breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones, together with the release of energy; destructive metabolism.
Homeostasis
the tendency toward a relatively stable equilibrium between interdependent elements, esp. as maintained by physiological processes.
Anabolism
the synthesis of complex molecules in living organisms from simpler ones together with the storage of energy; constructive metabolism
Metabolism
the chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life
Feedback
the modification or control of a process or system by its results or effects, e.g., in a biochemical pathway or behavioral response.
Positive
the enhancement or amplification of an effect by its own influence on the process that gives rise to it
Negative
the diminution or counteraction of an effect by its own influence on the process giving rise to it, as when a high level of a particular hormone in the blood may inhibit further secretion of that hormone, or where the result of a certain action may inhibit further performance of that action
Systems of A & P
Reproductive
Reporduction
Functional Unit: Gonads
Respiratory
Respiration
Reticuloendothelial
Assists Immune system
Protect against external invasion
Muscular
Support
Movement
Protection
Cardiovascular
Circulate blood
Transport nutrients and waste
Lymphatic
Immune Support
Cardiovascular Support
Digestive Support
Sensory
Gather Information
Integumentary
Remove Toxins
Digestive
Absorption of nutrients
Endocrine
Chemical Stability
Urinary
Eliminate waste
Functional Unit - Nephron
Nervous
Communication and Control
Immune
Protection from disease
Skeletal
Protection
Support
Lever of Movement
Storage of Minerals
Manufacture of Blood
Regions of the abdomen - Looking at the person
Right Hypochondriac - Epigastric - Left Hypochondriac
Right Lumbar - Umbilicus - Left Lumbar
Right Inguinal (Illiac) - Hypogastric - Left Inguinal (Illiac)
Proximal - Close to middle
Distal - From from middle
Supericial
Deep
Medial
Lateral
Central
Peripheral
Anterior / Ventral
Posterior / Dorsal
Superior
Inferior
Cephalic - Close to brain
Cranial - Close to skull
Caudal - At coccyx
Epi - Skin
Hypo - too little
Hyper - too much
Cardio - Heart
Mega - Big
Micro - Small
Rectomy - Surgical Removal
Bi - Two
Mono - One
Salpingo - Tube
oopho - Ovary
Deci = 1/10
Centi = 1/100
Milli = 1/1000
Deca = 10
Hecta = 100
Kilo = 1000
gram = weight
liter = volume
meter = distance
celsius/centigrade = temperature